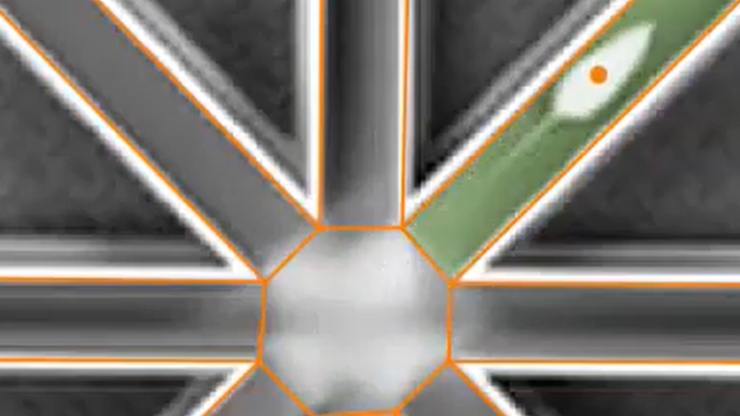
Managing your experimental design is crucial to successful automation of the Radial arm maze
ANY-maze is a great way to manage your experiments. Its intuitive design will help to walk you through your experimental plan and setup. This allows you to define each stage, the number of trials associated with it, the criterion for completion of the stage, etc.
This way you’ll always know which of your animals needs to be tested and where each animal is in its progression through a stage.
On the tabs below you'll find videos, recommended equipment and a list of results that are especially useful in the radial arm maze.
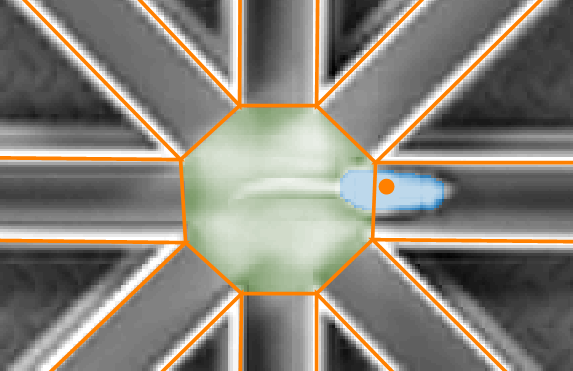
Precision tracking
ANY-maze’s whole body tracking allows you specify precisely when an arm entry should be scored.
For example, specifying an arm entry as occurring when 80% of the animal’s body is in the arm, equates very well with the traditional four-paws-in-the-arm rule. Watch the video to see this in action.
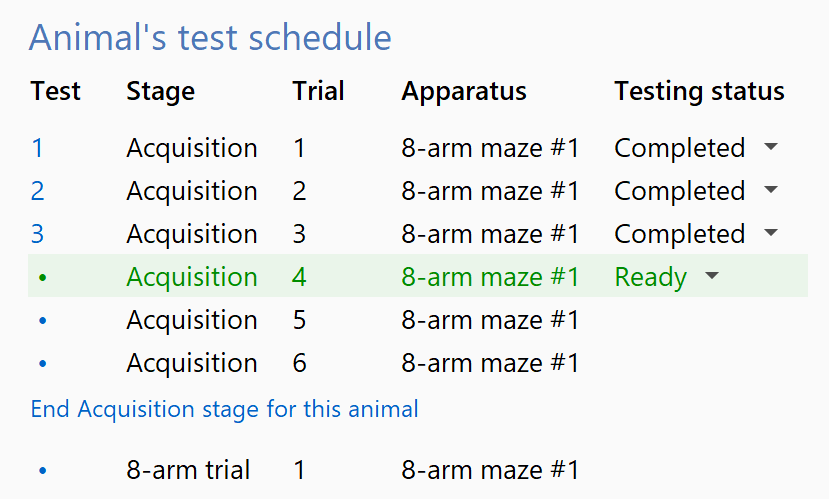
Keeping track of the specifics (managing stages and trials)
Radial arm maze experiments are usually comprised of a number of different stages (e.g. acquisition, 8-arm trial, 4-arm trial, etc.), with each stage including a number of repeated trials. ANY-maze allows you to specify your experimental design so that it is aware of and manages the different stages and the trials within them. This means that while running the tests, ANY-maze is automatically assessing training criteria to ensure you know which animal to test on which apparatus, for what purpose, stage and trial – as in the image on the right.
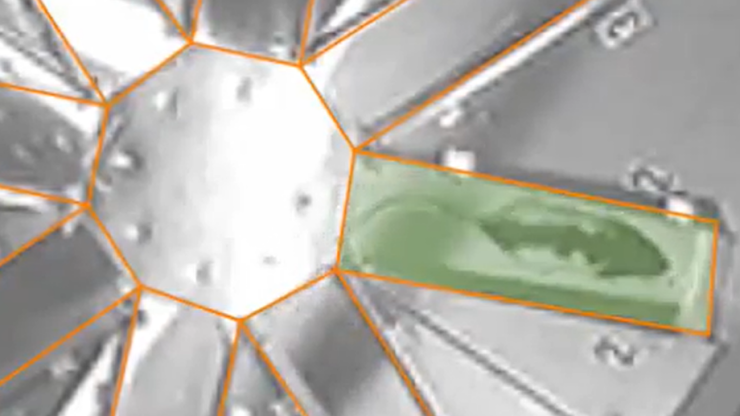
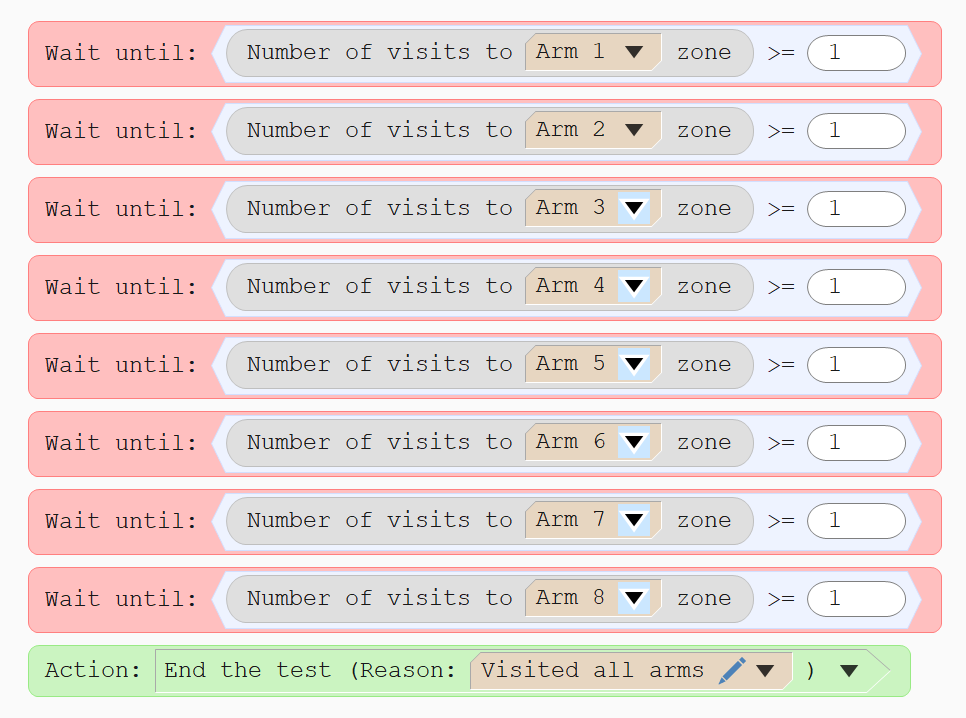
Detecting when the test is complete
A common task in the radial arm maze is to require the animal to visit every arm once; when it completes this task the test can end.
ANY-maze’s procedures are perfect for this – for example, the procedure on the right would end the test once the animal has visited all the arms of an 8-arm maze (Note that the order the animal visits the arms won’t actually matter)
Calculating results
ANY-maze will report a wide range of results for every arm in the maze, but in the Radial arm maze, you’re usually interested in results such as Working memory errors and Reference memory errors, which aren’t specific to any one arm.
This is where ANY-maze’s calculations come in useful. Calculations can derive new results from those ANY-maze already has, so for example, Working memory errors can easily be calculated based on the number of entries into each of the arms.

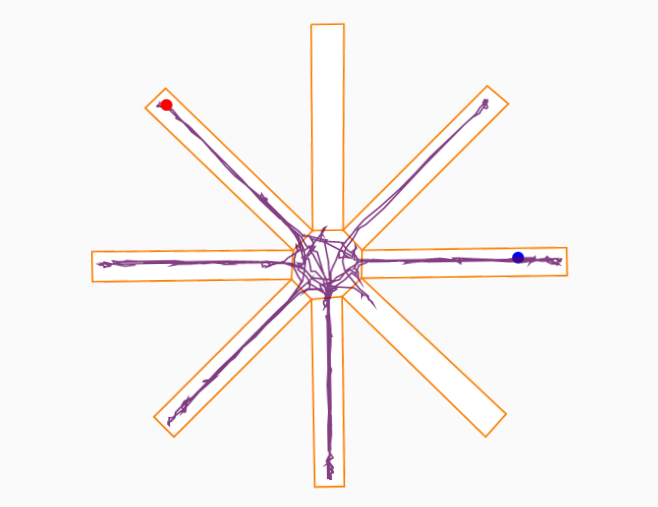
Viewing the animal's track
ANY-maze can plot the animal’s track around the maze which provides a great visual tool for both confirming the arms visited and for contrasting the behaviour of different animals.
Results
ANY-maze can provide literally hundreds of results for any test, but some of those that are commonly used in the Radial arm maze include:
- Test Duration
- Time in each of the arms
- Number of entries into each of the arms
- Sequential list of arm entries
- Spontaneous alternations
- Working memory errors (using a calculation)
- Reference memory errors (using a calculation)
- Total distance travelled
Tracking a Long-Evans rat in a reflective radial arm maze
In this example a Long-Evans rate was tested in a reflective metal 8-arm radial maze.
Despite the bright reflections and the fact that the animal is a non-uniform colour, ANY-maze tracks it well and correctly scores the arm entries in a way analogous to the four-paws-in-the-arm rule.
Tracking a white mouse in a unevenly lit radial arm maze
In this example a white coloured mouse was tested in a unevenly lit 8-arm radial maze, in which the centre is brighter than the arms. ANY-maze still tracks reliably and accurately detects the animal’s entries and exits to the arms using whole body tracking, which as can be seen, approximates well to the four-paws-in-the-arm rule.
Mazes
We manufacture our own 8- and 12-arm Radial mazes, both for Rat and Mouse. The walls slot into a grey non-reflective base plate and simply lift off for easy cleaning.
View more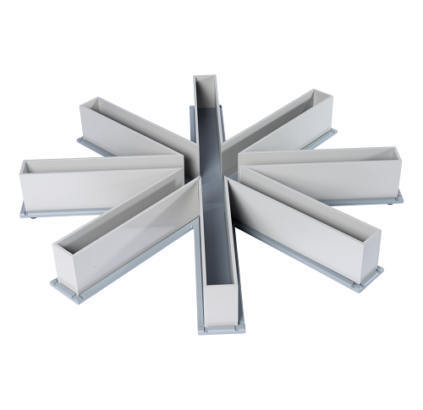
Cameras
USB Camera
The ANY-maze USB camera is an excellent choice for the Radial arm maze. We recommend fitting this camera with a varifocal (zoom) lens, so you can simply mount the camera on the ceiling and then zoom in and out until the maze nicely fits the camera's view.
View more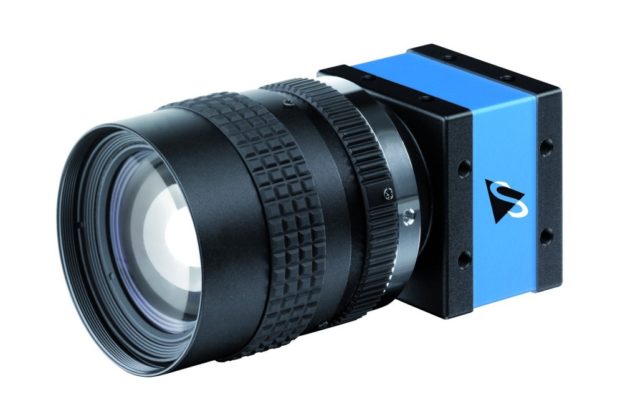
Web cam
A webcam is usually a good, and inexpensive, alternative choice for the Radial arm maze. If you intend to test in normal lighting conditions (>= 100 lux) and you can mount the camera far enough from the maze for it to see it all, then a webcam should work well.

Lighting
Infrared illuminator
If you intend to track in low light (< 10 lux) or in darkness, then you may wish to use an infrared illuminator and an infrared sensitive camera (most cameras are IR sensitive).
View more
Accessories
ANY‑maze Radio remote control
The ANY‑maze Radio remote control provides a convenient way to start the test as soon as the animal is in the maze. This remote works through walls and has 2 buttons, allowing you to control two apparatus independently.
View more
D’Adamo P et al. (2021) Inhibiting glycolysis rescues memory impairment in an intellectual disability Gdi1-null mouse; Metabolism Clinical and Experimental; 116
Tachi et al. (2021) Olanzapine attenuates postoperative cognitive dysfunction in adult rats; Heliyon; 7: E06218
Taneja K and Ganesh S (2021) Dendritic spine abnormalities correlate with behavioral and cognitive deficits in mouse models of Lafora disease. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 529: 1099-1120
Zhu L et al. (2020) Impaired Parahippocampal Gyrus–Orbitofrontal Cortex Circuit Associated with Visuospatial Memory Deficit as a Potential Biomarker and Interventional Approach for Alzheimer Disease. Neuroscience Bulletin. 36: 831-844
Jaeger ECB et al. (2020) Testosterone replacement causes dose-dependent improvements in spatial memory among aged male rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 113
Sharma S and Shukla S (2020) Effect of electromagnetic radiation on redox status, acetylcholine esterase activity and cellular damage contributing to the diminution of the brain working memory in rats. Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy. 106
Das S et al. (2019) CXCR7: A key neuroprotective molecule against alarmin HMGB1 mediated CNS pathophysiology and subsequent memory impairment. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity. 82:319-337
Kawase T and Furuse M (2019) Long-term administration of yoghurt improves spatial memory in mice. Journal of Pet Animal Nutrition. 22:1-13
Brose RD et al. (2019) Hydroxyurea improves spatial memory and cognitive plasticity in mice and has a mild effect on these parameters in a down syndrome mouse model. Front. Aging. Neuroscience. 11:1-14
R. M. Miller et al. (2018) Running exercise mitigates the negative consequences of chronic stress on dorsal hippocampal long-term potentiation in male mice; Neurobiology of Learning and Memory 2018; 149:28-38
F. Biundo et al. (2018) A role for tau in learning, memory and synaptic plasticity; Scientific Reports 2018; 8:3184
A. Shimbo et al. (2018) Mice lacking hippocampal left-right asymmetry show non-spatial learning deficits; Behavioural Brain Research 2018; 336:156-165
B.A. Wagner et al. (2018) Effects of testosterone dose on spatial memory among castrated adult male rats; Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018; 89:120-130
L.P. Li et al. (2018) PSD95 and nNOS interaction as a novel molecular target to modulate conditioned fear: relevance to PTSD; Translational Psychiatry 2018; 8:155
Hurst, Katrina, et al. (2017) A Putative Lysophosphatidylinositol Receptor GPR55 Modulates Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity. Hippocampus.
Brownlow ML et al. (2014) Partial rescue of memory deficits induced by calorie restriction in a mouse model of tau deposition. Behavioural Brain Research 271: 79-88
Sundaram JR et al. (2013) Specific Inhibition of p25/Cdk5 activity by the Cdk5 inhibitory peptide reduces neurodegeneration in vivo. The Journal of Neuroscience 33:334 –343
Wise LE et al. (2009) Hippocampal CB1 receptors mediate the memory impairing effects of ?9-Tetrahydrocannabinol. Neuropsychopharmacology 34: 2072–2080
Frye CA and Walf AA (2008) Progesterone enhances performance of aged mice in cortical or hippocampal tasks. Neuroscience Letters 437:116-20
Frye CA et al. (2007) Estrogens and progestins enhance spatial learning of intact and ovariectomized rats in the object placement task. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 88:208-16

 Setting up apparatus
Setting up apparatus Video capture & tracking
Video capture & tracking Observing behaviour
Observing behaviour Connecting equipment
Connecting equipment Automating complex tests
Automating complex tests Running tests
Running tests Results
Results Visualising data
Visualising data Analysis
Analysis Transferring data
Transferring data Open field
Open field Water-maze
Water-maze Y-maze
Y-maze Fear conditioning
Fear conditioning Novel object
Novel object Barnes maze
Barnes maze Radial arm maze
Radial arm maze Light/dark box
Light/dark box Operant conditioning
Operant conditioning Zebrafish
Zebrafish Computers
Computers Multifunction remote
Multifunction remote Accessories
Accessories Digital interface
Digital interface Optogenetic interface
Optogenetic interface Synchronisation interface
Synchronisation interface Relay interface
Relay interface Audio interface
Audio interface Touch interface
Touch interface Analogue interface
Analogue interface USB TTL cable
USB TTL cable Animal shocker
Animal shocker Components
Components Place preference
Place preference ANY-box
ANY-box T-maze
T-maze Zero maze
Zero maze Hole board
Hole board Sociability cage
Sociability cage OPAD
OPAD RAPC
RAPC Waterwheel forced swim test
Waterwheel forced swim test Thermal gradient ring
Thermal gradient ring Operon
Operon Activity Wheel
Activity Wheel Full ANY-maze licence
Full ANY-maze licence Other licence types
Other licence types Developing countries licence
Developing countries licence Contact support
Contact support Support Policy
Support Policy FAQs
FAQs Guides
Guides Downloads
Downloads Send us files
Send us files Activate a licence ID
Activate a licence ID Contact us
Contact us Blog
Blog About
About Testimonials
Testimonials Privacy Policy
Privacy Policy